Difference between revisions of "Mechanisms"
(→Levers) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
A crank is simply an off-center connection that provides energy to (or takes energy from) a rotating wheel. | A crank is simply an off-center connection that provides energy to (or takes energy from) a rotating wheel. | ||
| − | [[File:crank-animation.gif]] | + | [[File:crank-animation.gif| 300 px]] |
===Slider crank mechanisms=== | ===Slider crank mechanisms=== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
the lower the oscillation of the highest point of the red stick | the lower the oscillation of the highest point of the red stick | ||
| − | [[File:crank slider.gif]] | + | [[File:crank slider.gif| 300 px]] |
===Crankshaft=== | ===Crankshaft=== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
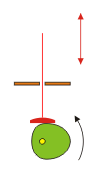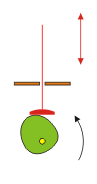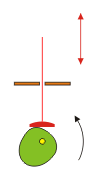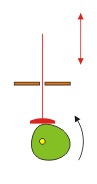
The larger the diameter of the wheel, the greater the vertical stroke of the red stick. | The larger the diameter of the wheel, the greater the vertical stroke of the red stick. | ||
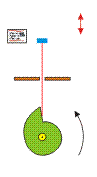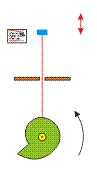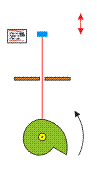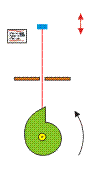
| − | [[File:crankshaft.gif]] | + | [[File:crankshaft.gif| 300 px]] |
==Linkages== | ==Linkages== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
They are use to change direction or amount of motion | They are use to change direction or amount of motion | ||
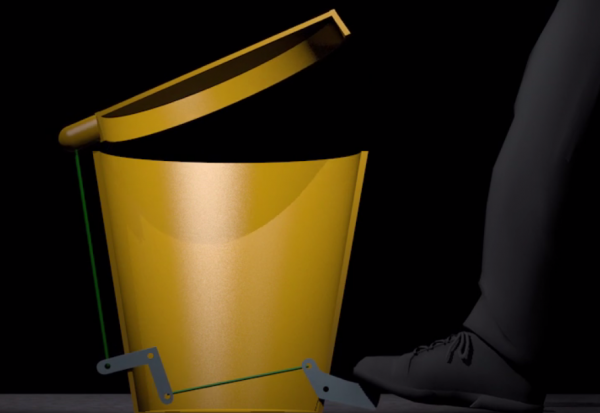
| − | [[File:trashbinlinlikage.png]] | + | [[File:trashbinlinlikage.png| 600 px]] |
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
| − | [[File:eccentriccam.gif]] | + | [[File:eccentriccam.gif| 300 px]] |
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
The shape of the cam creates a jump during the movement of the red stick. In this way can produce abrupt and sudden movements. | The shape of the cam creates a jump during the movement of the red stick. In this way can produce abrupt and sudden movements. | ||
| − | [[File:jumpingcam.gif]] | + | [[File:jumpingcam.gif| 300 px]] |
==Shafts== | ==Shafts== | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
| − | [[File:ratchet.gif]] | + | [[File:ratchet.gif| 300 px]] |
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
| − | [[File:Gear_reducer.gif]] | + | [[File:Gear_reducer.gif| 300 px]] |
Revision as of 07:08, 22 September 2016
Basic mechanisms
Levers
a lever is a rigid object with pivot point used to multiply the mechanical force of an object
it has input – pivot point-output
examples: seesaw hammer when removing nails crowbar also
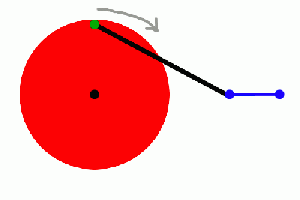
Cranks
A crank is simply an off-center connection that provides energy to (or takes energy from) a rotating wheel.
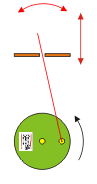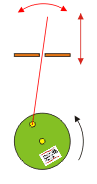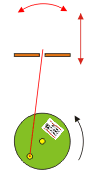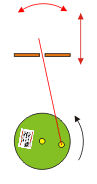
Slider crank mechanisms
he crank slider turns a circular motion in an oscillating movement and a vertical movement. The larger the distance between the wheel and the plane green brown, the lower the oscillation of the highest point of the red stick
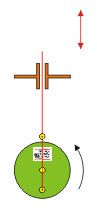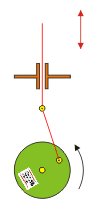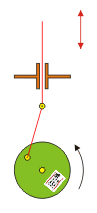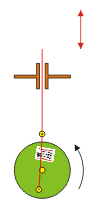
Crankshaft
The cam piston transforms a circular motion in a vertical movement. The larger the diameter of the wheel, the greater the vertical stroke of the red stick.
Linkages
we can use extra motion ( for exmple from a crank) to add extra movement
A linkage can be made from levers, cranks and connecting elements. They are use to change direction or amount of motion
Cams
Cams generally do the opposite job to cranks: they turn rotary motion into reciprocating motion.
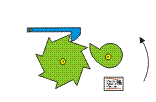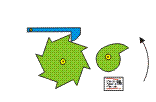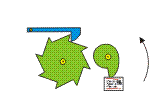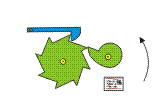
Eccentric cam
The eccentric cam transforms a circular motion in a vertical movement. the vertical excursion of the red stick changes as a function of the varying diameter of the cam.
Jumping Cam
The shape of the cam creates a jump during the movement of the red stick. In this way can produce abrupt and sudden movements.
Shafts
Ratchets
can be used to give intermittent or stepped motion. Also used to give rotation in one direction only
The cam rotates the large wheel of an eighth for each revolution. The blue slider prevents the large wheel can turn in the opposite.
Gearing
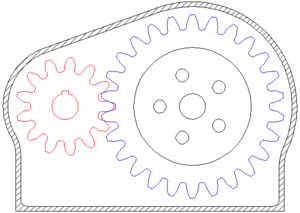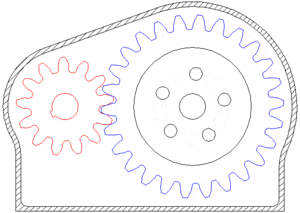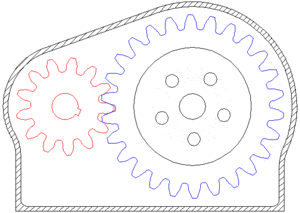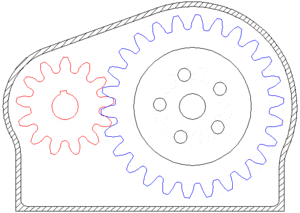
A gear or cogwheel is a rotating machine part having cut teeth, or cogs, which mesh with another toothed part to transmit torque.
Geared devices can change the speed and power delivered.
GEAR RATIO
two gears, one half as big as the other, have a gear ratio of 2:1. The smaller gear has to spin twice to cover the same distance covered when the larger gear spins once.
Drives
A drive is a method of connection rotation shafts together
the drive can involve gearing, changing direction or rotation of the shafts.
A bike chain is a POSITIVE DRIVE ...it cannot slip ( it is kept locked to the sprocket wheel ) , while wheels slip if they are under resistance ( break) and they stop turning, that is FRICTION, pulleys also work by friction.