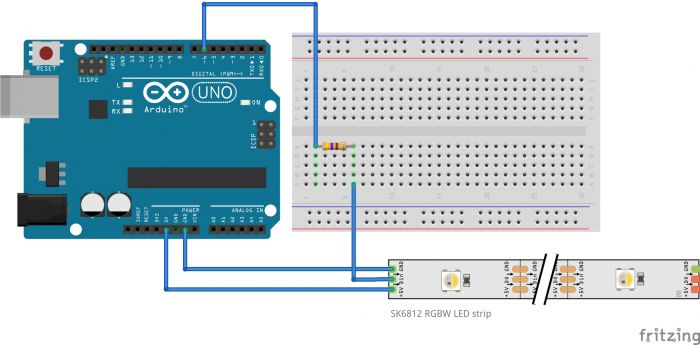
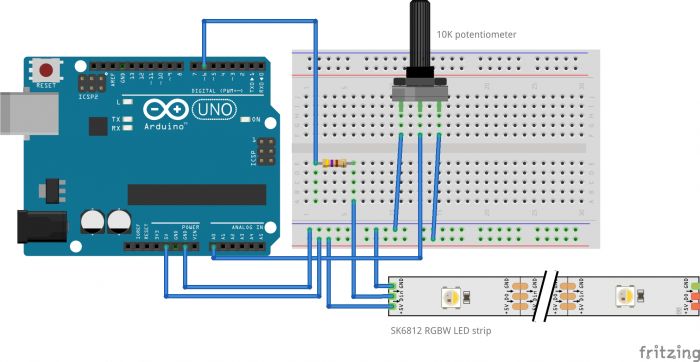
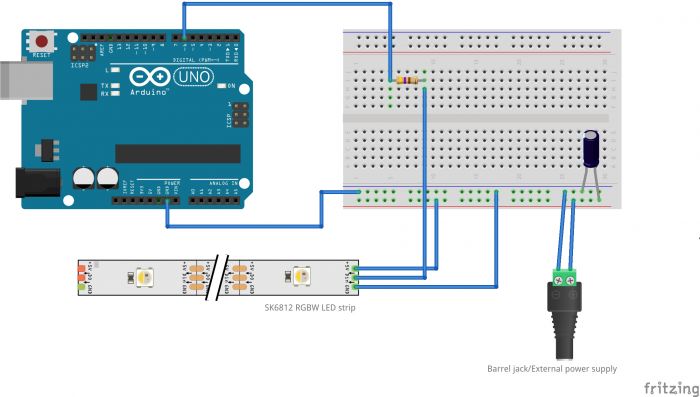
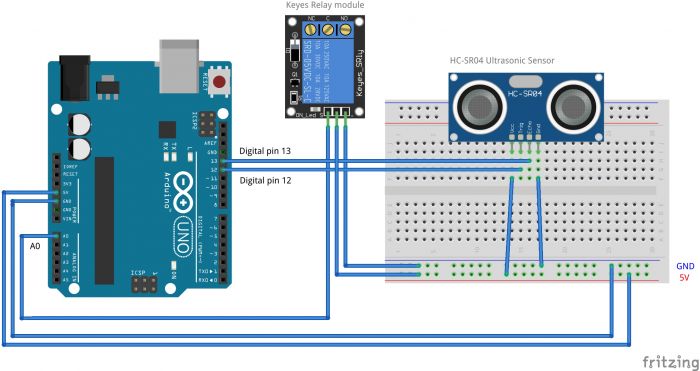
Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with Arduino & Lights"
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
== Arduino and LEDs== | == Arduino and LEDs== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Leds.gif|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
===The LED=== | ===The LED=== | ||
| − | What is an LED? | + | What is an LED?<br> |
| − | LED is short for light emitting diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows | + | LED is short for light emitting diode, is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it. Light is produced when the particles that carry the current (electrons and holes) combine together within the semiconductor material.<br> |
| + | LEDs come in different colors. Different semiconductor materials with different bandgaps (separation of the bands containing electrons and holes) produce different colors of light.<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Anodecathode.jpeg|600px]]<br> | ||
| + | In an LED, energy flows in one direction, generating the luminous effect at the top, where the semiconductor is. | ||
| + | LEDs have two legs, corresponding to the positive and negative side, also known as Anode and Cathode. These can be distinguished because the positive leg, the Anode, is longer than the other one. If we connect these two poles to a battery, the LED will turn on. <br> | ||
| + | [[File:Battery_led.gif|200px]] | ||
| + | ===Arduino: how does it work=== | ||
| + | Arduino is a microcontroller, a type of device, like a computer, designed to operate simple tasks. | ||
| + | board | ||
| + | software | ||
| + | breadboard | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
board | board | ||
===Connecting the LED to Arduino=== | ===Connecting the LED to Arduino=== | ||
| − | |||
[[File:Led_one.jpg|600px]] | [[File:Led_one.jpg|600px]] | ||
| + | For this you will need: | ||
| + | <div style="font-family:monospace"> | ||
| + | * Arduino board | ||
| + | * a 220 ohm resistor | ||
| + | * an LED | ||
| + | * jumper wires | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | ===Programming the LED=== | ||
| + | ==== Open Arduino IDE==== | ||
| + | To program your board you can use [https://www.arduino.cc/en/software Arduino's own software] that allows use to write code and upload it on the board. | ||
| − | === | + | Make sure that your board is connected before |
| − | + | ====LED Blink==== | |
| + | ====LED Fade==== | ||
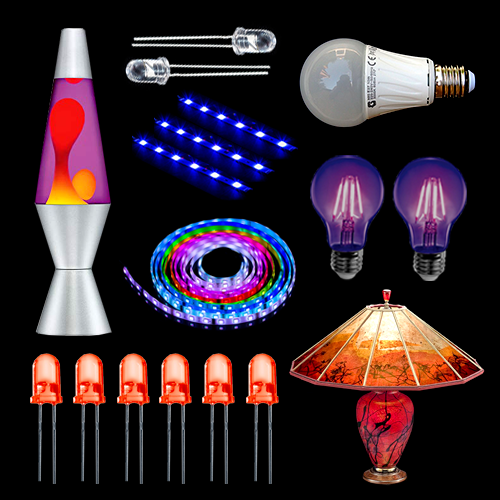
===LEDs traffic light=== | ===LEDs traffic light=== | ||
[[File:Led_traffic_lights.jpg|600px]] | [[File:Led_traffic_lights.jpg|600px]] | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 14 April 2023
Introduction
Are planning to add light to your work?
Do you want the light source in your installation to be controlled by sensor data?
Are you curious about the possibilities of programming lights with Arduino?
During this station skill, you will be introduced to some standard methods of programming lights with Arduino.
Arduino is a microcontroller that makes it easy for us to work with different kinds of hardware like lights, motors and a wide array of sensors. During this station skill, we will use it to work with lights.
We will do this during three sessions, each one focused on working with different kinds of lights: LEDs, LED strips and light bulbs.
Station Skill schedule
Week: 16
Date Fri 21 Apr 2023
Time 09:00-12:00
Arduino & LEDs
Week: 17
Date Fri 28 Apr 2023
Time 09:00-12:00
Arduino & LED strips
Week: 19
Date Sat 13 May 2023
Time 09:00-12:00
Arduino & Relays
Session 1
What can you do with it?
Examples
- Soliloquy, Tromarama, 2018
- wave is my nature, vtol, 2015
- Game of me, Xuanning Chen
- Healer, Pamela Ronsenkranz
- Alain Le Boucher
- Collection of light, Humans since 1982, 2011
- Tatsuo Miyajima
Life (le corps sans organes) - https://tatsuomiyajima.com/work-projects/life-le-corps-sans-organes-no-17-2013-no-10-2014/
Arduino and LEDs
The LED
What is an LED?
LED is short for light emitting diode, is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it. Light is produced when the particles that carry the current (electrons and holes) combine together within the semiconductor material.
LEDs come in different colors. Different semiconductor materials with different bandgaps (separation of the bands containing electrons and holes) produce different colors of light.
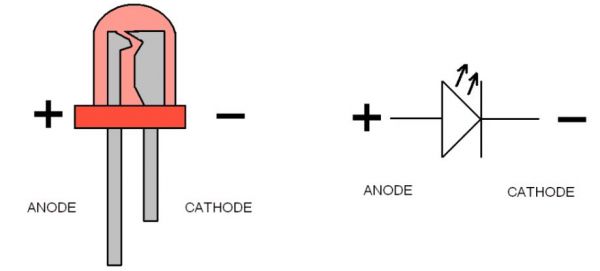
In an LED, energy flows in one direction, generating the luminous effect at the top, where the semiconductor is.
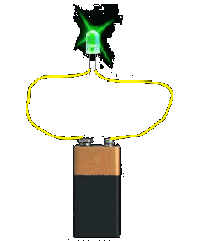
LEDs have two legs, corresponding to the positive and negative side, also known as Anode and Cathode. These can be distinguished because the positive leg, the Anode, is longer than the other one. If we connect these two poles to a battery, the LED will turn on.
Arduino: how does it work
Arduino is a microcontroller, a type of device, like a computer, designed to operate simple tasks. board software breadboard
board
Connecting the LED to Arduino
- Arduino board
- a 220 ohm resistor
- an LED
- jumper wires
Programming the LED
Open Arduino IDE
To program your board you can use Arduino's own software that allows use to write code and upload it on the board.
Make sure that your board is connected before
LED Blink
LED Fade
LEDs traffic light
LED Morse code
Resources/More
Arduino reference page more leds : series parallel circuit, calculating resistance
Session 2
Arduino and LED strips
Examples of work
Types of strips
addressable, rgb, one color