Difference between revisions of "Thermistor"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
Then, the Steinhart-Hart equation is used to convert the resistance of the thermistor to a temperature reading. | Then, the Steinhart-Hart equation is used to convert the resistance of the thermistor to a temperature reading. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
[[File:Thermistor01.png]] | [[File:Thermistor01.png]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=c style="border:3px dashed pink"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | int ThermistorPin = 0; //// which analog pin to connect | ||
| + | int Vo; | ||
| + | float R1 = 10000; | ||
| + | float logR2, R2, T, Tc; | ||
| + | float c1 = 1.009249522e-03, c2 = 2.378405444e-04, c3 = 2.019202697e-07; | ||
| + | |||
| + | void setup() { | ||
| + | Serial.begin(9600); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | void loop() { | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vo = analogRead(ThermistorPin); | ||
| + | R2 = R1 * (1023.0 / (float)Vo - 1.0); | ||
| + | logR2 = log(R2); | ||
| + | T = (1.0 / (c1 + c2*logR2 + c3*logR2*logR2*logR2)); | ||
| + | Tc = T - 273.15; | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.print("Temperature: "); | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.print(Tc); | ||
| + | Serial.println(" C"); | ||
| + | |||
| + | delay(500); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 28 March 2018
Using a Thermistor (temperature sensor)
In short: Thermistors change resistance with a change in temperature.
They are classified by the way their resistance responds to temperature changes. In Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors, resistance decreases with an increase in temperature. In Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors, resistance increases with an increase in temperature. In this example we are using an NTC thermistor.
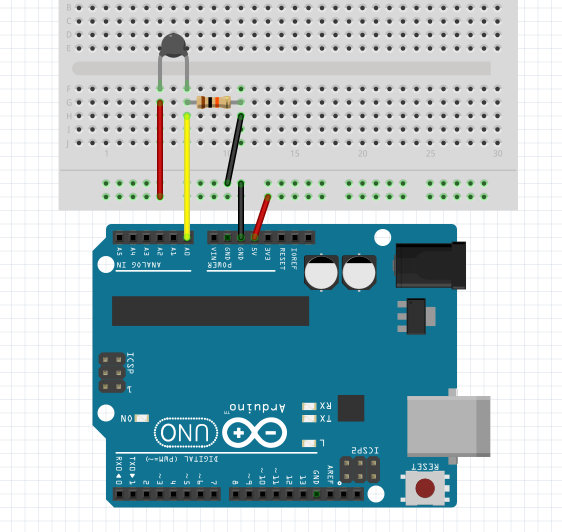
Since the thermistor is a variable resistor, we’ll need to measure the resistance before we can calculate the temperature. However, the Arduino can’t measure resistance directly, it can only measure voltage.
The Arduino will measure the voltage at a point between the thermistor and a known resistor. This is known as a voltage divider.
Then, the Steinhart-Hart equation is used to convert the resistance of the thermistor to a temperature reading.
int ThermistorPin = 0; //// which analog pin to connect
int Vo;
float R1 = 10000;
float logR2, R2, T, Tc;
float c1 = 1.009249522e-03, c2 = 2.378405444e-04, c3 = 2.019202697e-07;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
Vo = analogRead(ThermistorPin);
R2 = R1 * (1023.0 / (float)Vo - 1.0);
logR2 = log(R2);
T = (1.0 / (c1 + c2*logR2 + c3*logR2*logR2*logR2));
Tc = T - 273.15;
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(Tc);
Serial.println(" C");
delay(500);
}