Difference between revisions of "Energy for Designers"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="border-style: solid; border-width: 20px" | {| class="wikitable" style="border-style: solid; border-width: 20px" | ||
| − | | [[File:pauline.png|200px]] | [[File:dance.png|200px]] | + | | [[File:pauline.png|200px]] |
| + | |[[File:dance.png|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Pauline van Dongen, solar garment | |Pauline van Dongen, solar garment | ||
Revision as of 07:13, 26 January 2019
Energy for Designers intro
Energy is one of the big challenges of our society to be solved by you as an inventor designer. We will be trying out weird ways to generate and harvest energy, like algae, chocolate, dance floor, mud, a Joule Thief, body heat and ice. We will also compare this to energy made with a potato, a solar cell, a wind turbine. Or just hack and be an energy parasite! With this experience, you will experiment further and connect your source of energy to your design idea. This can be a product, fashion, or a drawing, illustration, a knitting, architecture or a poster.
What is energy?
Cappuccino Energy 47 kcal = 197 kJ (per 100 ml) 12 minutes vacuum cleaning Smart phone battery: 47.5 kJ = 10 kcal
Big energy for heating houses, cities.
Small energy for your own gadgets and hacks and smart textiles, or charging your smart phones.
Nano energy, from plants, algae, bacteria.
Designer and Artist examples
Pauline van Dongen, solar garment charging your cell phone in 2 days

|

|
| Pauline van Dongen, solar garment
charging your cell phone in 2 days |
Sustainable dance floor |
Parasites of wasted energy in the city experimental setups, making use of heat outlets, running streetcars/trams, wind in the metro, wifi energy

|

|
Week 1 - Day 1
The link to the ppt will be provided soon (if this wiki wants to eat my file...)
A Dutch windmill in action [1]
How the people in the Middle Ages managed to lift stones to make cathedrals - big wheels, not for running mice, but running men!
My toy steam engine is running on a blower [2]
A steam engine is making movement from heating Because we are nowadays doing everything electrically we have nearly forgotten "movement" as "energy"
Potato power
A potato is so nice! Because it is a battery with it's own skin The "power" is a bit limited though, even in series
Getting energy out of ice and my hand - energy harvesting with a Peltier element [3]
This is called energy harvesting My hand is not a good source of energy The heat from my hand connected to ice can make an LED blink But then it gets cold fast
Solar cells of course.
Hand crank devices
Plant power (indicating a voltage and a current, but there is no "power")...

Some current |

Some voltage |
Discussion: We also talked about this question: What is more interesting for a designer... Something that works or something that maybe (not) works For example, a solar cell (works) or a plant (who knows if it works)
Week 1 - Day 2
Technical day:
You have to know 2 laws to be able to do some calculations of electrical energy Ohms law V = I * R Power law P = V * I The laws seem to be simple, but the combinations, in series and in parallel for example make life a bit more complicated.
Basic electronics, Soldering
Basic calculations, numbers
Consider the energy required to heat 1.0 kg of water from 0 oC to 100 oC when the specific heat of water is 4.19 kJ/kgoC: Q = (4.19 kJ/kgoC) (1.0 kg) ((100 oC) - (0 oC)) = 419 (kJ) equivalent to 100 kcalori (food units)
Banana 93 kcal = 390 kJ One banana = boiling water for one cup of tea (1/4 of a liter)
lifting a mass of 100 kg an elevation of 10 m = 9810 J = 10 kJ Pro 20 climbing stairs = 5 kcal = 20 kJ. 15 Minutes Walking around 50 kcal = 200 kJ
Smart phone battery 3300 mAH -> 4Volt * 3.3A * 3600 (seconds) = 47.5 kJ roughly equal to about 1/8 of a banana
The energy by mass of gasoline is over 12,000Wh/kg. In contrast, a modern Li-ion battery only carries a bout 200Wh/kg; (https://batteryuniversity.com/index.php/learn/article/comparing_the_battery_with_other_power_sources But there are all sorts of “problems”, you never get full energy out of something!
Batteries, 3V, 1.5V, power of a battery
Lipo, power cells
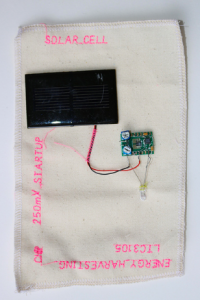
Joule Thief experiments - boosting voltage
Potato battery
Mud Algae, plant - cell battery
Bike dynamo set up
Hand charging devices IKEA made
Solar cell examples IKEA

Soldering, ppt: |
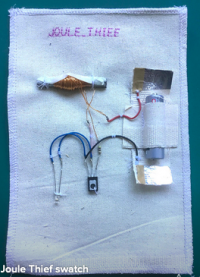
We made a Joule Thief, boosting device, ppt: |

|
Week 1 - Day 3
Starting your own assignment considerations
Making the paper generator

https://makezine.com/projects/power-paper-circuits-with-static-electricity/ https://makezine.com/2013/10/10/new-technology-paper-generators-harvest-static-electricity/ |
Finishing the Joule Thief
Week 1 - Day 4
Working on your own
Week 1 - Day 5
Working on your own
Week 2 - Day 1
Tutoring
Intro microcontrollers
Adding sensors to a microcontroller

Pressure sensor |

Temperature sensor |

Light Sensor |
Week 2 - Day 2
Working on your own
Week 2 - Day 3
Tutoring
Week 2 - Day 4
Working on your own
Finishing, testing
Week 2 - Day 5
Presentation day!