How it's made 2223
__ __ _ __ _ __
/ / / /___ _ __ (_) /( )_____ ____ ___ ____ _____/ /__
/ /_/ / __ \ | /| / / / / __/// ___/ / __ `__ \/ __ `/ __ / _ \
/ __ / /_/ / |/ |/ / / / /_ (__ ) / / / / / / /_/ / /_/ / __/
/_/ /_/\____/|__/|__/ /_/\__/ /____/ /_/ /_/ /_/\__,_/\__,_/\___/
2022-09-08
- WH.02.125 (Prototyping Space IAS) 9:00 - 16:00
Introduction
1. Circuit bending
2. Introduction Arduino
Hello World!
void setup() {
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Hello World!"); //sends a message to the computer
}
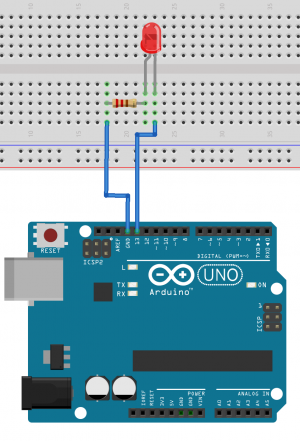
Simple Led blink example
int ledPin = 13; //the int ledPin is 13
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin,OUTPUT); //ledPin is a OUTPUT
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin,HIGH); //turns pin 13 on
delay(500); //stops the loop for 500 milliseconds
digitalWrite(ledPin,LOW); //turns pin 13 off
delay(500); //stops the loop for 500 milliseconds
}
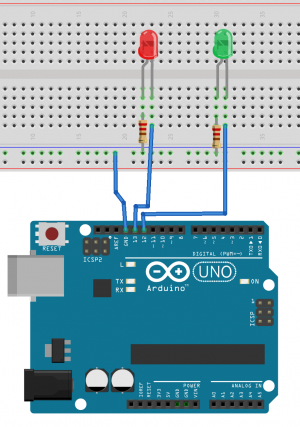
Traffic light example
int RedLedPin = 13; //the int RedLedPin is 13
int GreenLedPin = 12; //the int GreenLedPin is 12
void setup() {
pinMode(RedLedPin,OUTPUT); //ledPin is a OUTPUT
pinMode(GreenLedPin,OUTPUT); //ledPin is a OUTPUT
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(GreenLedPin,HIGH); //turns green led on
delay(5000); //stops the loop for 5000 milliseconds
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ //this for loop gets 5 times repeated
digitalWrite(GreenLedPin,LOW); //turns green led off
delay(500); //stops the loop for 500 milliseconds
digitalWrite(GreenLedPin,HIGH); //turns green led off
delay(500); //stops the loop for 500 milliseconds
}
digitalWrite(GreenLedPin,LOW); //turns green led off
digitalWrite(RedLedPin,HIGH); //turns red led on
delay(5000); //stops the loop for 5000 milliseconds
digitalWrite(RedLedPin,LOW); //turns red led on
}
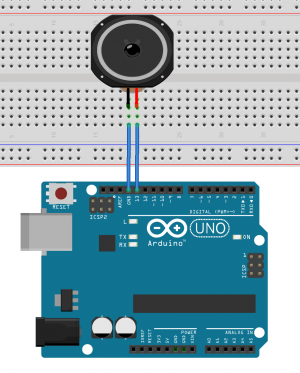
Speaker example
int speaker = 13; //int speaker is 13
void setup() {
pinMode(speaker, OUTPUT); //pin 13 is an output
}
void loop() {
for(int i = 100; i< 1000;i++){ //for loop counts from 100 to 1000
tone(speaker, i); //generates a tone on pin 13 with the frequency of int i
delay(10); //stops the code for 10 milliseconds
}
}
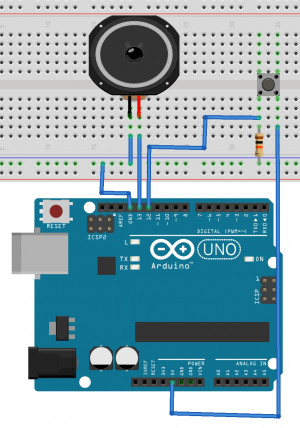
Speaker and button example
//code generates on button press a random tone
int speaker = 13; //int speaker is 13
int button = 12; //int speaker is 12
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); //makes a serial connection to the computer
pinMode(speaker, OUTPUT); //pin 13 is an output
pinMode(button, OUTPUT); //pin 12 is an output
}
void loop() {
bool buttonState = digitalRead(button); //reads pin 12 & bool is a on or off value
if(buttonState == HIGH){ //if the button is HIGH(pressed)
int randomValue = random(100,1000); // creates an int called randomValue with a random value between 100 and 1000
tone(speaker, randomValue); //creates an tone on pin 13 with the random value as frequency
delay(500); //stops the loop for 500 milliseconds
}
}
2022-09-15
- WH.02.125 (Prototyping Space IAS) 10:00 - 16:00
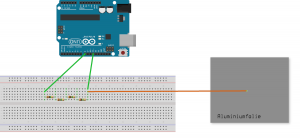
Capacitive Sensor printing values to Serial Monitor
#include <CapacitiveSensor.h>
CapacitiveSensor sensor = CapacitiveSensor(8,11);
long raw;
void setup(){
sensor.set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(0xFFFFFFFF);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("raw");
}
void loop(){
raw = sensor.capacitiveSensor(10);
Serial.println(raw);
delay(10);
}
Theremin
#include <CapacitiveSensor.h>
CapacitiveSensor sensor = CapacitiveSensor(8,11);
int speaker = 13; //connect a speaker between pin 13 and GND
long raw;
void setup(){
sensor.set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(0xFFFFFFFF);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("raw");
}
void loop(){
raw = sensor.capacitiveSensor(10); //lowest 450 & highest 750
raw = min(raw, 750); //max value of raw is 750
raw = max(raw, 10); //min value of raw is 10
long speakerValue = map(raw,450,750,100,4000); //scales to value from 450 and 750 to 100 and 4000
tone(speaker,speakerValue); //plays the frequency (raw) on port 13(speaker)
Serial.print(raw);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(speakerValue);
}
Capactive sensor as button
#include <CapacitiveSensor.h>
CapacitiveSensor sensor = CapacitiveSensor(8,11);
int speaker = 13;
long raw;
void setup(){
sensor.set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(0xFFFFFFFF);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("raw");
}
void loop(){
raw = sensor.capacitiveSensor(10); //lowest 450 & highest 750
if(raw > 600){ //if raw is bigger than 600
Serial.println("touched"); //print "touched"
tone(speaker,440); //play a tone with 440 hz
delay(1000); //stop 1000 second
noTone(speaker); //stop playing the tone
}
delay(10);
}
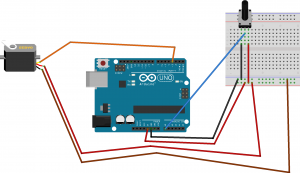
Servo motor movement between 0 and 90 degrees
//this example controls a standard servo motor and moves it between 0 and 90 degrees
//the servo has three different wires
//the red wire is plus and connected to 5v
//the brown wire is minus and connected to GND
//the orange wire is the signal wire and connected to pin 3 (remember the ~-symbol - it means PWM)
#include <Servo.h>
Servo theServo;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
theServo.attach(3);
}
void loop() {
for(int i = 0; i < 90; i++){
theServo.write(i);
Serial.println(i);
delay(50);
}
for(int i = 90; i > 0; i--){
theServo.write(i);
Serial.println(i);
delay(10);
}
}
automatic trash can - servo motor connected capactive sensor
#include <Servo.h>
#include <CapacitiveSensor.h>
CapacitiveSensor sensor = CapacitiveSensor(8,11);
Servo theServo;
long raw;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
theServo.attach(3);
sensor.set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(0xFFFFFFFF);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("raw");
}
void loop() {
raw = sensor.capacitiveSensor(10); //lowest 450 & highest 750
if(raw > 600){ //if raw is bigger than 600
open(); //do void open
delay(4000); //wait for 4 seconds
close(); //close void opne
}
}
void open(){
//open
for(int i = 0; i < 90; i++){ //count from 0 to 90
theServo.write(i); //move the servo from 0 to 90
Serial.println(i);
delay(50);
}
}
void close(){
//close
for(int i = 90; i > 0; i--){
theServo.write(i);
Serial.println(i);
delay(10);
}
}
trash can controlled by serial commands
//in this sketch the servo is controlled by serial commands from the computer
//if you send the letter "o" to the arudino it will execute "void open()"
//if you send the letter "c" to the arduino it will execute "void close()"
#include <Servo.h> //import the servo library
Servo theServo; //create a servo
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); //serial connection
theServo.attach(3); //theServo is at port 3 (remeber the ~(PWM)-Symbol
}
void loop() {
if(Serial.available()){ //if there is a serial command comming
char command = Serial.read(); //read the serial command
if(command == 'o'){ //is the command and 'o'
open(); //do void open
}
if(command == 'c'){
close();
}
}
}
void open(){
//open
for(int i = 0; i < 90; i++){ //count from 0 to 90 with int i
theServo.write(i); //i is the servo position
Serial.println(i); //print the servo position to the serial monitor
delay(50); //wait for 50 milliseconds
}
}
void close(){
//close
for(int i = 90; i > 0; i--){
theServo.write(i);
Serial.println(i);
delay(10);
}
}
Potentiometer opening the trash can
//in this sketch the servo is controlled by an potentiometer
//a potentiometer is a variable resistor that can be changed by rotation
#include <Servo.h> //import the servo library
Servo theServo; //create a servo
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); //serial connection
theServo.attach(3); //theServo is at port 3 (remeber the ~(PWM)-Symbol
}
void loop() {
int value = analogRead(A0); //read the analog pin A0 the value is between 0 and 1023
value = map(value,0,1023,0,180); //adjust value from 0 to 1023 to 0 and 180 because the servo works with degrees
theServo.write(value);
}
2022-09-22
- WH.02.110 (Instruction Room IAS) 10:00 - 16:00
presentation
Desinger with unconventional approaches:
- Enzo Mari - Autoprogettazione? (pdf)
- Christian Kuhtz - Einfälle statt Abfälle (ideas against trash) (link to website)
Unconventional projects with microcontrollers:
painting machine
//in this sketch one poti controls one servo
#include <Servo.h>
Servo jointOne;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("start");
jointOne.attach(10);
}
void loop() {
int value = analogRead(A0);
value = map(value, 0, 1023, 0, 180);
jointOne.write(value);
delay(10);
}
2022-09-29
- WH.02.110 (Instruction Room IAS) 10:00 - 16:00
Motor control
//connect the dc-motor to the motorshield motor port 1
//connect a external power source
#include <Adafruit_MotorShield.h>
Adafruit_MotorShield AFMS = Adafruit_MotorShield();
Adafruit_DCMotor *myMotor = AFMS.getMotor(1);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
AFMS.begin();
myMotor->setSpeed(200);
myMotor->run(RELEASE);
}
void loop() {
myMotor->run(FORWARD); //forward
myMotor->setSpeed(255); //max speed
delay(2000);
myMotor->run(RELEASE); //break
delay(2000);
myMotor->run(BACKWARD); //backward
myMotor->setSpeed(255); //max speed
delay(2000);
myMotor->run(RELEASE); //break
delay(2000);
}
2022-10-06
* WH.02.110 (Instruction Room IAS) 9:00 - 16:00
2022-10-13
* WH.02.110 (Instruction Room IAS) 9:00 - 16:00