How it's made
Physical computing
Basic electronics and circuits
Basic electronic components and sensors
Arduino introduction
all about microcontrollers
simple circuit and sketches
Sensors and Actuators
Sensing
we often construct our reality using our sensory experience:
our visual and sound come from our eyes and ears, we can feel the moisture level on our skins, we can feel the gravity and orientation thanks to our inner ear structures.
and now imagine all the sensory input can be converted into digits and feed to a computer, and the computer device can decide what to do(output) with the input data. let's look back to the Shannon-Weaver model of communication.
there is so many already made sensor module for Arduino. Many sensors can detect signals or pick up data beyond human senses. For example ultrasonic sensors.
Imagine we can use these sensor technologies to expand our senses and "reality".
Back to the Sensors: In General, there are two types of sensors: analog and digital.
The analog sensor can detect a range of data. (for example from 0-1020)
The digital sensor can detect either 0 or 1. (or HIGHT /LOW).
for better understanding: the analog sensor is like a dimmer and the digital sensor is like a normal switch.
Here is a list of sensors and examples:
'''Comment sensors:''' Don't need additional libraries, normally included in Arduino's example tutorials.
Potential meters: AnalogReadSerial Botton or switch: Button Ultrasonic sensor: Ping Mic or piezo: knock toneMultiple
Flex & force sensor: toneKeyboard LDR (Light Dependent Resistor): Calibration tonePitchFollower
Need to install additional libraries.
Capacitive Sensor-Analog : adafruit-cap1188-breakout Or touch-board Pulse sensor(heart rate): pulsesensor UV sensor: uv-index-sensor Gyroscope/acceleration meter:Gyroscope/acceleration
Actuators with Adafruit Motor Shield
DC motor
push-pull solenoid
Servo motor
Stepper motor
TIP 120 circuit
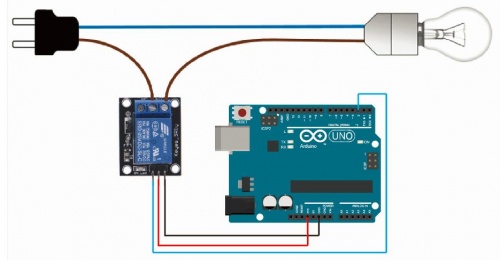
Relay Module
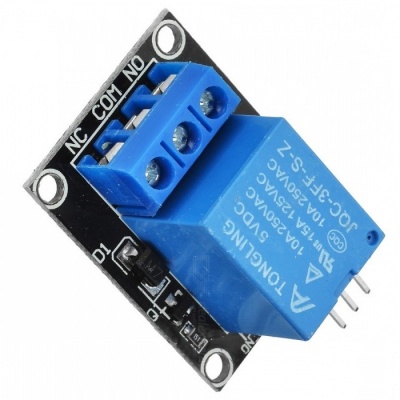
Introducing the Relay Module
A relay is an electrically operated switch. It means that it can be turned on or off, letting the current go through or not.
Controlling a relay with the Arduino is as simple as controlling an output such as an LED.
Notice the writing on the module terminals
COM: common pin
NO (Normally Open): there is no contact between the common pin and the normally open pin. So, when you trigger the relay, it connects to the COM pin, and supply is provided to a load
NC (Normally Closed): there is contact between the common pin and the normally closed pin. There is always a connection between the COM and NC pins, even when the relay is turned off. When you trigger the relay, the circuit is opened and there is no supply provided to a load.
If you want to control a lamp, for example, it is better to use a normally open circuit, because we just want to light up the lamp occasionally.
it is very straightforward as you can see. But always double-check the relay module connections before you plug things together.
GND: goes to ground
VCC: goes to 5V
IN1: controls the relay (it is connected to an Arduino digital pin)