Servo motor
Now we will hookup a servo motor and instruct it to behave a certain way.

This is a servo, a very small one
Hookup
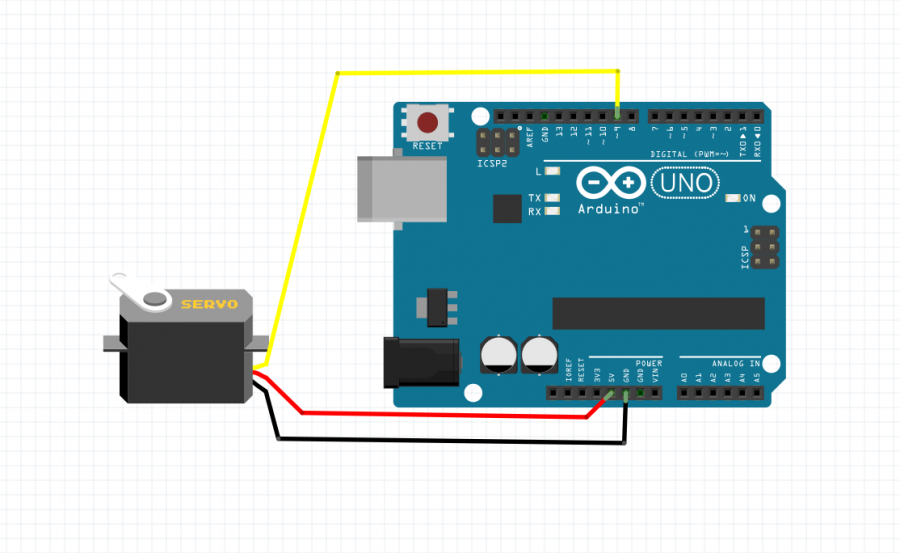
The servo has 3 wires, we need to connect them all to the Arduino.
red is for 5V
you will find it easy to plug one end of a jumper wire inside the connectors of the servo motor, and the other end to the corresponding pin of the Arduino make sure you use corresponding colors for the jumpers, in bigget setups messy wire can cause you more time to debug
black is for GND
to GND of the Arduino
and orange is for signal
signal is going into the pin of the Arduino we will use to control the servo motor We will look for a pin that has a wave next to the number ( look at the Arduino board). Those pins are able to output Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a fancy term for describing a type of digital signal. Pulse width modulation is used in a variety of applications including sophisticated control circuitry. Also in our case control the servo motor. The control wire is used to send this pulse. For more info how servos work look here [[1]]
We will use another example to see if our servos work
Sweep
Now with knowing where the examples are located, find a servo example sketch called sweep.
you should have a code that looks like this
/* Sweep
by BARRAGAN <http://barraganstudio.com>
This example code is in the public domain.
modified 8 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Sweep
*/
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
for (pos = 0; pos <= 180; pos += 1) { // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees
// in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
for (pos = 180; pos >= 0; pos -= 1) { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
}
Let's upload the sketch to the board
Observe the motor---->sweeping?
Knob
Great,
let us include another agent into the servo situation.
A potentiometer to exercise some external control
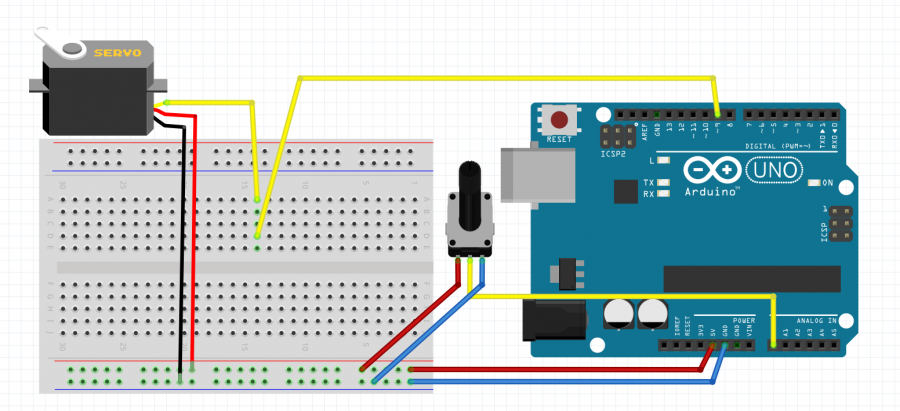
/*
Controlling a servo position using a potentiometer (variable resistor)
by Michal Rinott <http://people.interaction-ivrea.it/m.rinott>
modified on 8 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Knob
*/
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int potpin = 0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer
int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
val = analogRead(potpin); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023)
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
myservo.write(val); // sets the servo position according to the scaled value
delay(15); // waits for the servo to get there
}
Servo and LDR
where problems with data start to appear.
constraining...and then...
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
int mappedVal;
int constrainedVal;
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
val = analogRead(A0); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023)
mappedVal = map(val, yourMinVal, yourMaxVal, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
// in case the sensor value is outside the range seen during calibration
constrainedVal = constrain(mappedVal, 0, 180);
myservo.write(constrainedVal); // sets the servo position according to the scaled value
delay(15); // waits for the servo to get there
}
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
int mappedVal;
int constrainedVal;
int newval;
int oldval;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
val = analogRead(A0); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023)
mappedVal = map(val, 470, 840, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
newval = constrain(mappedVal, 0, 180);
if (newval < (oldval - 15) || newval > (oldval + 15)) { //dead band setup
myservo.write(newval);
Serial.println(newval);
oldval = newval;
delay(15);
}
}