Using the CNC mill
1. Designing the PCB
There are several ways for designing PCB. For example you can use the following softwares:
- Fritzing (easy to use) https://fritzing.org/
- Kicad (more professional) https://www.kicad.org/
Lets start with Fritzing.
All the Fritzing Tutorials
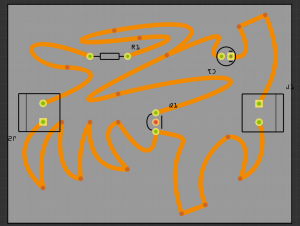
pcb design basic tutorial
Designing a custom shape pcb
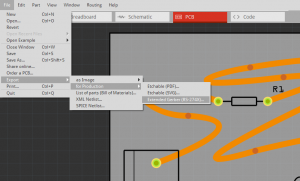
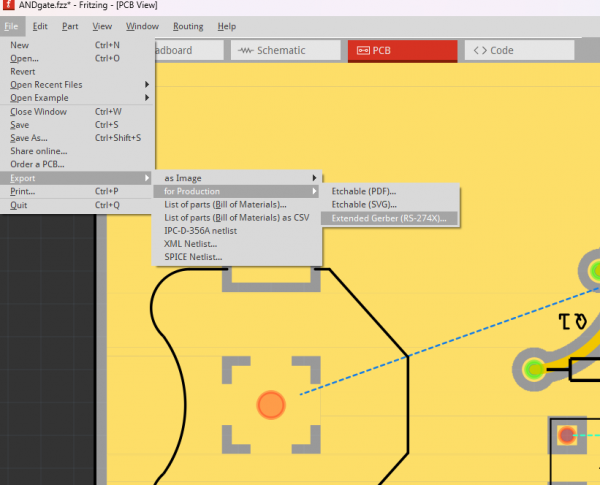
That looks already quite good. After you finished the PCBs you have to export it as a "Extender Gerber (RS-274X)"-Format! Select the folder where you would like to save it.
2. Generating the G-code
In this step you have to generate G-code with the Gerber files. G-code or sometimes called nc-code (numeric controll code) tells the CNC mill when to turn on the spindle or to which position it should move.
We will use FlatCam (http://flatcam.org/) to generate the G-Code.
The Flatcam manual
- Start FlatCAM
- Go to Edit -> Preferences and make sure measurements are set to millimeters.
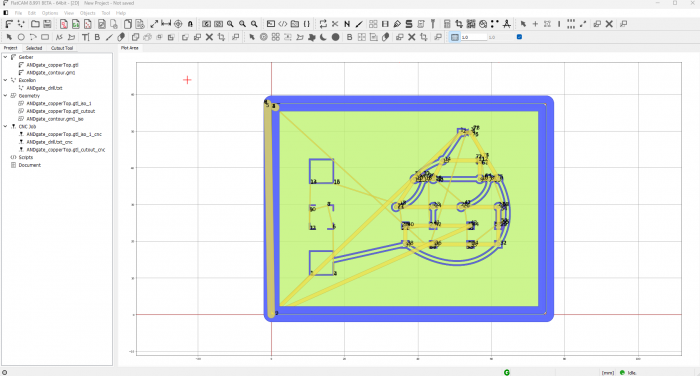
To mill a circuit board, we will need to make three separate files, the traces, the holes and the contour.
TRACES
First for the traces:
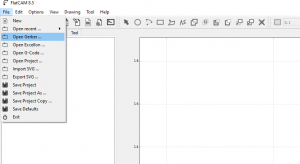
- Click on [File] -> [Open Gerber ...]
- Select the ".gbl" (copper bottom) file
- Now select the file in the Project list and click on [selected]
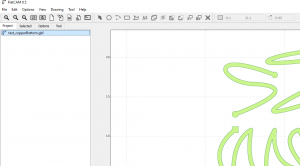
- drag in "copperBottom.gbl"
- Double click on the Gerber file to go to the Selected tab.
Set the Tool Settings to:
- Tool dia: 0,5000
- #Passes : 1
- Passes overlap: 0,00000%
and Click "Generate Isolation Geometry"
Here we will set the millings settings.
Under Parameters for Tool 1
- Cut Z: -0.0800
- Uncheck Multi-Depth (default)
- Travel-Z: 2,0000 (default)
- Uncheck Tool Change (default)
- End-move Z: 50,0000
- Feedrate X-Y: 120,0000 (default)
- Feedrate Z: 60,0000 (default)
- Spindle speed: 0 (default)
Click on "Generate CNCJob object" and "Save CNC Code"
<HOLES>
To drill out the holes, we'll need to import your drill.txt file. Go to Files > Open > Open Excellon and navigate to your drill.txt file.
Go to Project and double click the "drill.txt" under Excellon.
The settings for the drill bit are:
- Cut Z: -2,0000 (default)
- Travel Z: 2,0000 (default)
- Uncheck Tool Change (default)
- End move Z: 50,0000
- Feedrate Z: 30,0000 (default)
Click "Create Drills GCode"
If you see huge yellow circles , lower the size to 1 if you see huge yellow circles underneath the "CNC Tools Table" and click "Update Plot".
Scroll down and click "Save CNC Code".
CONTOURS
Lastly we want to mill out the shape of the PCB.
Go to File > Open > Open Gerber and navigate to "contour.gm1"
Open the file and double click it to go to the "Selected" tab.
Select "Cutout Tool"
Object to be cutout: "contour.gm1"
Object kind: Single (default)
- Tool Diameter: 1
- Cut Z: -1,8 (default)
- Check Multi-Depth: 0,6 (default)
- Margin: 0 (default)
- Gap Size: 2
- Gaps:4 (default)
(not necessary if your circuit board is taped to the sacrificial layer properly, but if you don't mind breaking some tabs it's a safe option)
Now select "Generate Freeform Geometry"
Tools Table:
1,0000 | C1
Parameters for Tool 1:
- Cut Z: -1,8 (default)
- Multi Depth: 0,6000 (default)
- Travel Z: 2,0000
- End move Z: 50,0000
- Feedrate X-Y: 120,0000
- Feedrate Z: 60,0000
- Spindle speed: 0 (default)
- Uncheck Dwell (default)
- Postprocessor: default (default)
Now select "Generate CNCJob object"
and click "Save CNC Code".
Flatcam 8.991 Overview
There is a good, concise tutorial for this Flatcam version here Flatcam single layer pcb tutorial
3. Milling the PCB
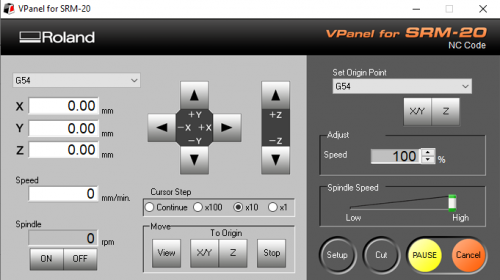
Start the program "V-Panel for SRM-20", make sure the mill is turned on and the lid is closed.
TRACES
We'll start by milling out the traces. To do this, we need to make sure the V-shaped bit is installed in the CNC. The V-shaped bit can be found in the CNC box and should look like this:
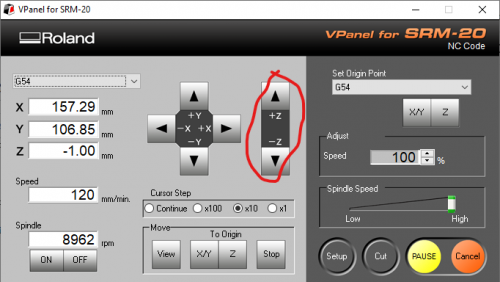
We start installing the V-shaped bit by moving the CNC-head all the way up. In V-Panel, you can do this by pressing the UP arrow with "+Z" next to it.
When the CNC head is all the way up, replace the mill unscrewing the screw holding the mill bit on the side of the CNC-head.
Now install the V-shaped bit and tighten the screw with the hex key.
Calibrating the CNC for your circuit"
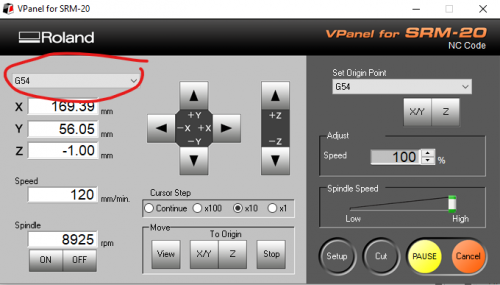
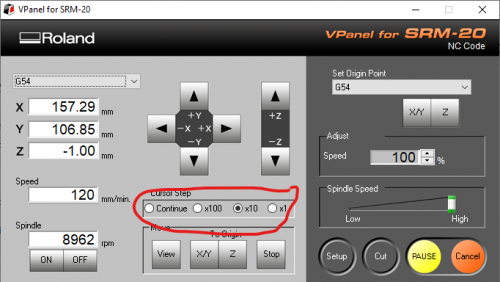
To properly mill out the traces, we need the CNC to know where the face is it needs to mill. To do this Change the Machine Coordinate System on the top left to G54:
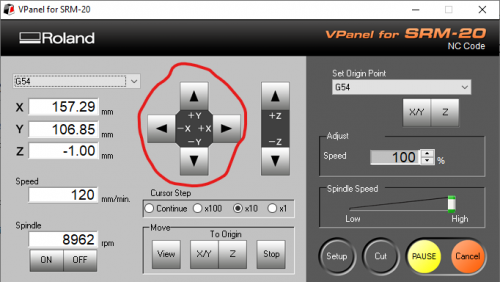
and move the Mill all the way to the bottom left corner of your copper plate using the arrows.
Now drop down the mill with the Z-arrows until almost touch the surface. !! Be careful not to hit the surface!! You will break the mill.
Make more precise adjustment by changing the Cursor step.
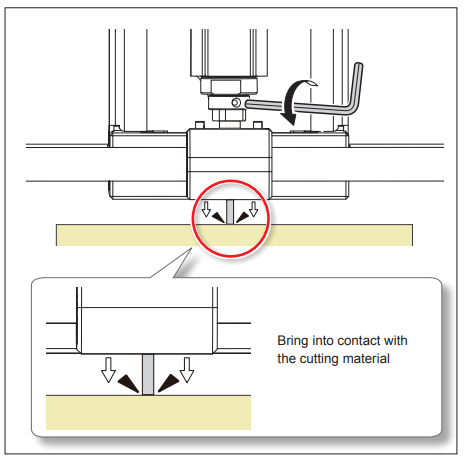
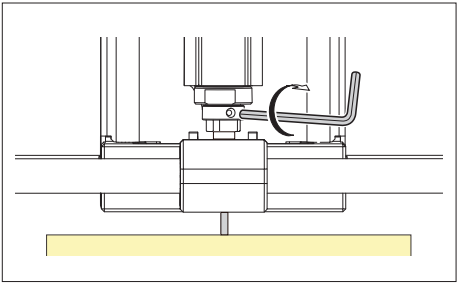
When you are as close as possible to the surface. Unscrew the mill with the small hex key, let it drop
and tighten it again.
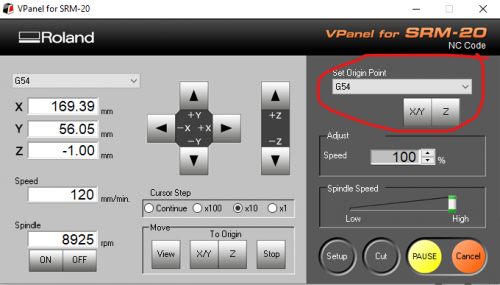
Now set the new origin point to G54 and click X/Y and Z.
X, Y, Z should now be 0, 0, 0.
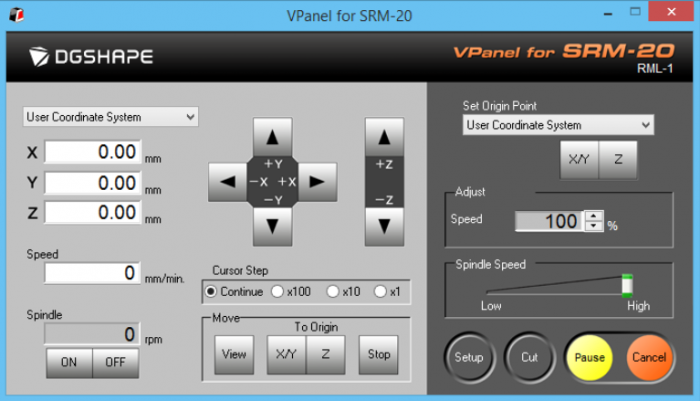
Using the Vpanel software to run the machine
Whenever you use a new bit, calibrate the Z value for the new bit. You do this by installing the bit and its socket with the wrenches in the box and a Allen wrench.
The V-shaped bit is used for milling out the traces and the mill bit for the holes and contours. The V-shaped bit needs the big socket and the mill bit the medium sized one.
You calibrate the bit bit installing it. Going all the way down, as far as you can and undoing the screw inside the socket to loosen up the bit. It will drop down as far as it can. Tighten it again, and press the "Z" button on the right (at Set Origin Point)". You can do the same for X/Y axis if you want the script to start at a specific point.
When the CNC is calibrated, select the "Cut" button on the bottom right and Add your .NC file. Press output to start the Milling. Mill your traces first, then your holes and then the contours for the best stability and do all of these individually so you can switch bits in-between.
Good luck!
5.Trough-hole pcb with Fritzing for Mods
As mentioned, when using Kikad or Eagle it is relatively easy to export each layer as a .svg or .png file, when using Fritzing and having a through-hole component, we will use a slightly more bulky pipeline. In Fritzing it is all very straight forward if you have only surface mount components, but gets complex to export an image file with just holes.
Thus we go through a slightly more complex pipeline of two more pieces of software.
We will export gerber files from Fritzing
Then we will use a gerber viewing software (Gerbv [1]) or gerberlogix (https://www.easylogix.de/products_detail.php?prog_id=1) to view our
- bottom copper .gbl file
- our contour .gml file
- our drills .txt file
We will then export each layer we need as separate image files (.png or .svg)
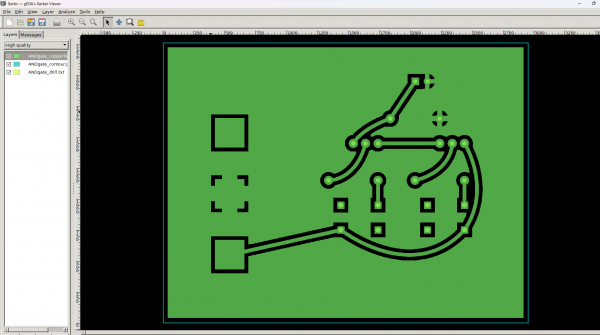
And then last, before we can go to Mods we will use Gimp or Photoshop to convert images to black and white and also do some editing if we have a ground pour.
Only then, we will move to Mods.
Tutorial: Surfacing the CNC bed
4. Using Mods
Alternatively we can use Mods (web based software from Fab Academy) to generate paths from .SVG or .PNG files
When using Kikad or Eagle it is relatively easy to export each layer as a .svg or .png file, when using Fritzing and having a through-hole component, we will use a slightly more bulky pipeline.
Mods project is a module based software with a web interface that already has a SRM-20 preset
Here is a good in depth tutorial how to use it but bare in mind that the interface has changed a bit and you may find differences
Here is an even longer tutorial including the finishing and soldering of a board